Match the Level of Protein Structure With the Correct Description
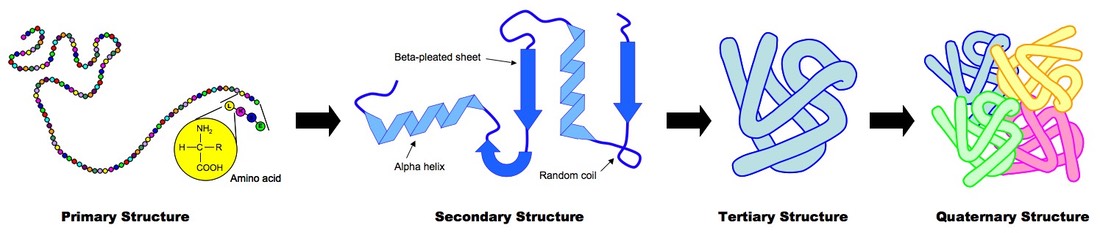
Select all that apply. Secondary structure is the next level up from the primary structure and is the regular folding of regions into specific structural patterns within one polypeptide chain.

Kinematics Motion Graph Matching Card Game Motion Graphs Persuasive Writing Prompts Physics And Mathematics
QuatenaryHere is the list of options1.

. Match the following molecules with their function. Quaternary 10 The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. Select the characteristics of chaperone proteins.
- Contains heptad repeats. 1 The protein to consider here is collagen. The secondary structure consists of local packing of polypeptide chain into α-helices and β-sheets due to hydrogen bonds between peptide bond central carbon backbone.
The formation of a protein is created using a hierarchy of structures. Answer 1 of 2. Further bending and coiling of protiens into fibrous o bonds attraction of hydrogen bonds globular shapes.
Match each example or description with the corresponding level of protein structure. The insulin molecule shown here is cow insulin although its structure is similar to that of human insulin. MRNA Translated into proteins 3.
These are called the primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structures of the. NAD and FAD Transport electrons What facts would you select to show the major significance of the element carbon in. The folding of a protein chain is however further constrained by many different sets of weak noncovalent bonds that form between one part of the chain and another.
These involve atoms in the polypeptide backbone as well as atoms in the amino acid side chains. Secondary structure IV v The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide II. 500 points Match each example or description with the corresponding level of protein structure.
The four levels of protein structure are distinguished from one another by the degree of complexity in the polypeptide chain. 2 There may be several answers for some of these. A single protein molecule may contain one or more of the protein structure types.
For example the hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains A and B shown in diagram below. DNA Contain genes that can be transcribed 2. Match the type of protein structure to its correct descriptiona.
Formed by noncovalent interactions between two or more polypeptide chains. Hydrogen bonds between polar amino acids ionic bonds covalent bonds between sulphur containing amino acids hydrophobic interactions between non-polar amino acids. Coiling and folding of peptides held together by the C.
QUESTION 20 Match the level of protein structure to the correct description Secordary structure Primary structure A. Determines how the protein will fold into a unique three-dimensional structure. Tertiary structure The spatial arrangement of all polypeptide chains III.
Match each example or description with the corresponding level of protein structure. - The three dimensional structure of a protein made of 1 polypeptide - Complexes of 2 3 4 etc protein molecules are called dimers trimers tetramersoligomers - Oligomers may be. Match the protein to the descriptions.
Secondary structure - consists mostly of hydrogen bonds between local areas of a protein sequence. Formed from interactions between R-groups. The sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chains.
The primary structure of protein is the hierarchys basic level and is the particular linear sequence of amino acids comprising one polypeptide chain. Match each description to its correct level of protein structure. The sequence of amino repeated pattern of only found in proteins results from hydrogen acids in the alpha-helix coiling or folding within composed of more bonds between polar polypeptide.
Give the name of the fourth protein structure and what makes it. Match each description to the correct level of protein structure. No partial credit.
The weak bonds are of three types. -They are used both to accomplish the original folding of proteins and to restore the structure of incorrectly folded proteins. The simplest level of protein structure primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain.
Select the disease type that could result from a deficiency in chaperone proteins. Primary structure - consists of covalent peptide bonds between amino acids. Proteins have four levels of organization.
Made of 2 or more polypeptides. Hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl oxygen and the. Primary structure refers to the linear sequence of the amino acids connected by the peptide bonds.
The location of prosthetic groups is shown. This is also known as the sequence of the protein. Sequence of amino acids held together by peptide B.
Quaternary structure The local conformation of the polypeptide backbone IV. The hydrogen bonds frequently occur between back. By convention four levels of protein organization may be identified.
- Contains Glycine at every 3rd residue. -They have been found in virtually every organism that has been examined. The complete three-dimensional conformation of a polypeptide II.
Match each level of protein structure with its description A. ATP Provide energy for cell activities 4. Match each example or description with the corresponding level of protein structure.
- Contains intrachain hydrogen bonds. 11 The 3-D shape of the polypeptide C. O Formed with identical protein monomers HOMOOLIGOMER o Formed with different protein monomers HETEROOLIGOMERS o Example.
Hydrogen bonds ionic bonds and van der Waals attractions as explained in. What are the four the.

Levels Of Protein Organization
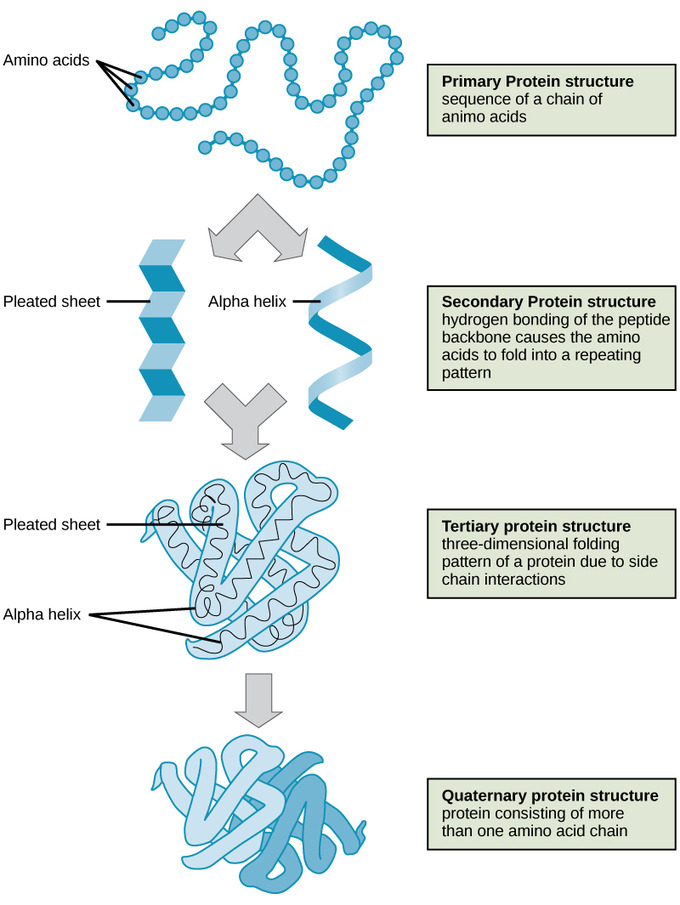
Protein Structure Boundless Chemistry

Cell Structure Practice Pdf Cell Structure Beginning Of School Prokaryotes

Create A Protein Project Introducing Miraclin Students Used Tangle Toys To Construct An Imaginary Protein Detaili High School Biology Tangle Toy Biology

Levels Of Protein Organization

Enzymes Doodle Docs Biology Worksheet Biology Activity Enzymes Biology
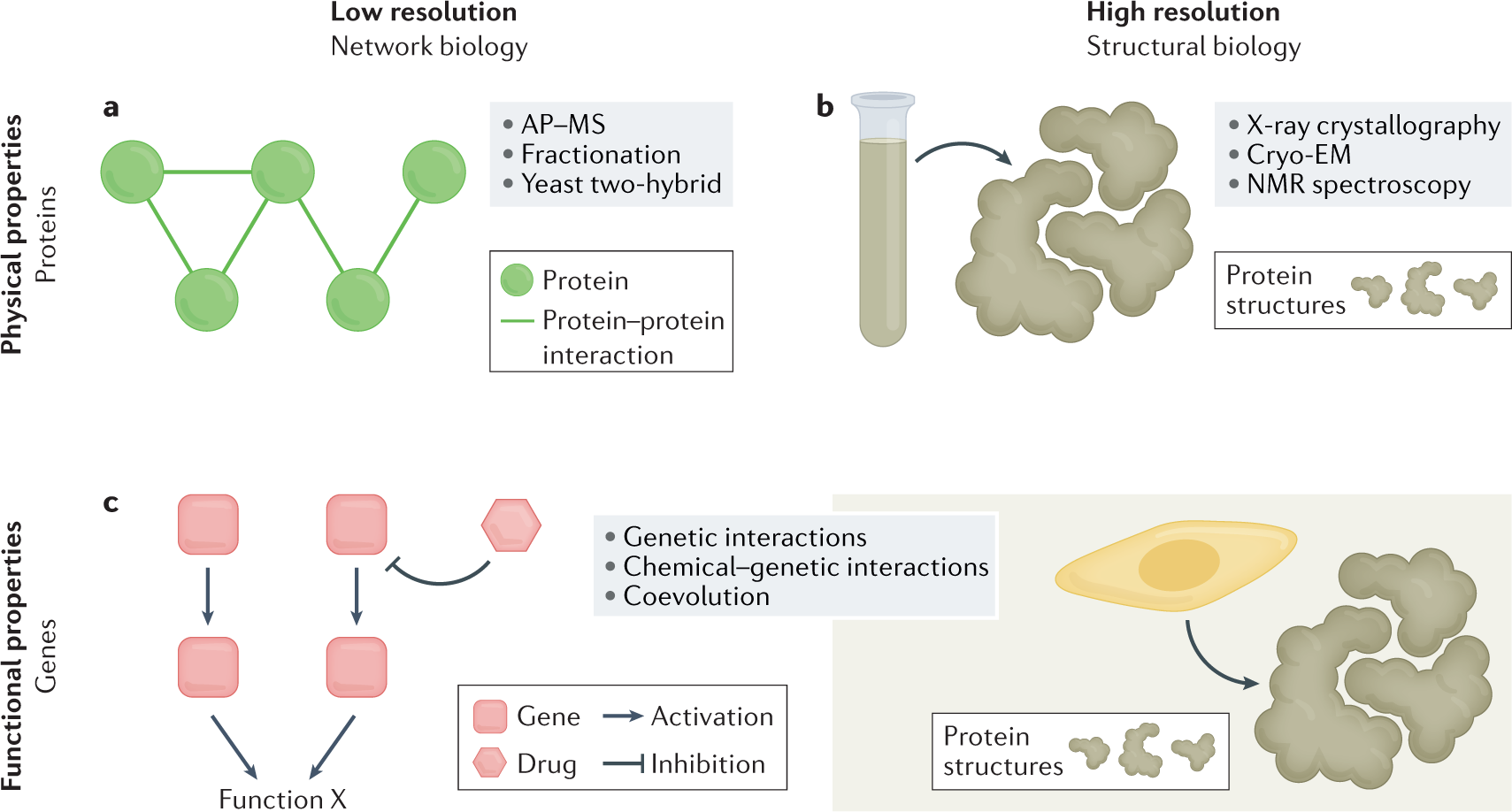
From Systems To Structure Using Genetic Data To Model Protein Structures Nature Reviews Genetics

Levels Of Protein Organization

Structural Classification Of Proteins Database An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Biol Chapter 3 Review Flashcards Quizlet

Interpro In 2019 Improving Coverage Classification And Access To Protein Sequence Annotations Superfamily Protein Sequence Segmentation
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry

Chapter 5 Mastering Biology Flashcards Quizlet
Chapter 2 Protein Structure Chemistry

Dna Structure And Function Quiz Dna Lesson Plans Biology Worksheet Printable Worksheets

Genetics Differentiated Vocabulary Distance Learning Life Science Lessons Genetics Vocabulary

Classification Of Lipids Chemistry Education Biochemistry Notes Study Biology

Image Result For Cell Membrane Worksheet Cell Membrane Coloring Worksheet Cells Worksheet Cell Membrane Structure
Comments
Post a Comment